Effective Radius
and Underpressure of an
Air Extraction Well in a Heterogeneous Porous Medium
Stephan Schumacher
and Marian Slodicka
Transport in Porous Media. 29(3):323-340, 1997.
By soil venting, the extraction probes can get the air from
passive wells or through the soil surface. In this situation, most of
the air enters the soil in the vicinity of the probes.
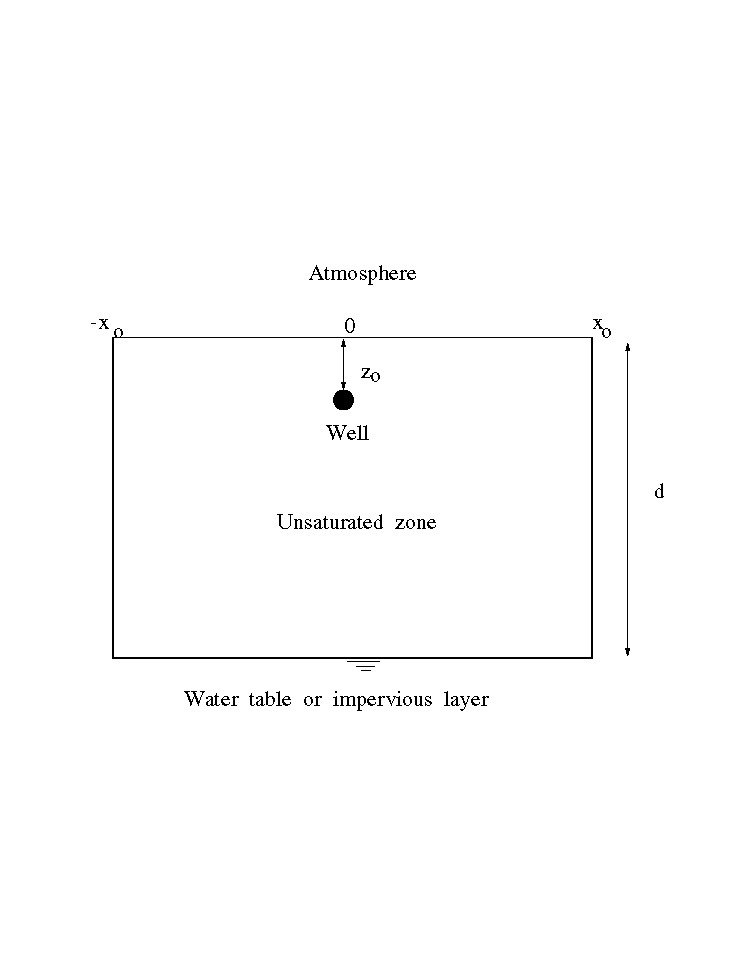
The radius of a circle (on the ground surface
around the vertical well axis) through which 90 % of the air
flows is called the Effective Radius.
For a homogeneous soil matrix it can
be computed analytically.
The effective radius gives an estimate for a reasonable distance
between neighboring active wells.
The relation between the pressure at a well and its discharge
depends on the
air permeability of a soil. The dependence can be used in order to
- give an estimate for the pressure necessary to induce a
prescribed discharge if
the permeability is known
- derive permeability values from pumping experiments.
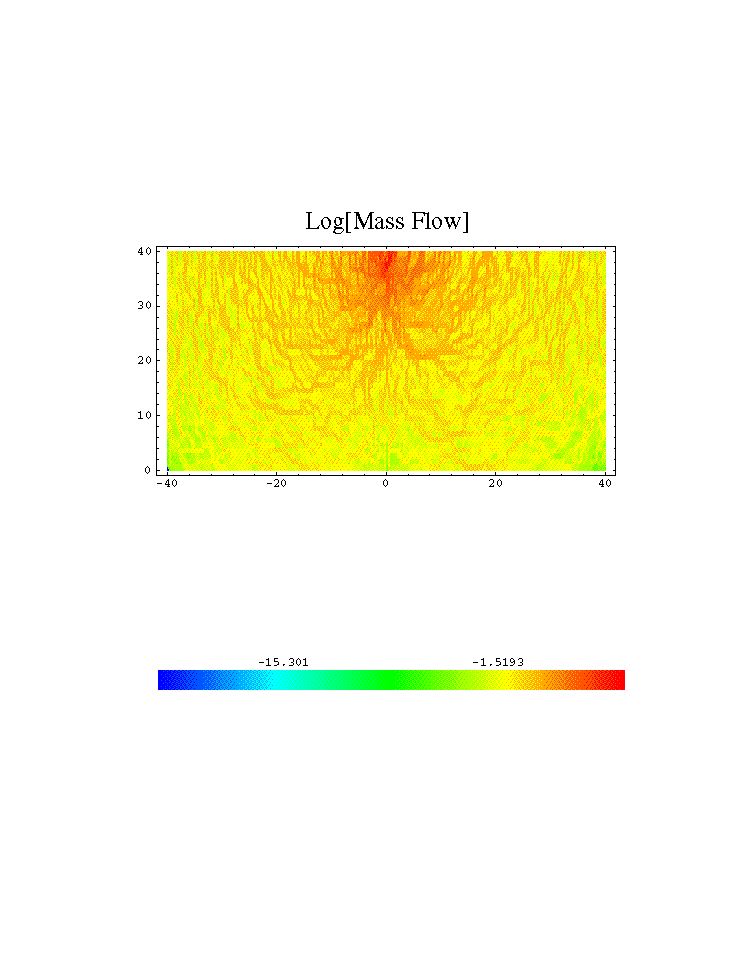 For a random heterogeneous soil matrix, the existence of
high permeable channels has an influence
on the effective radius and the air pressure at the well.
Thus, stochastic distributions and the average values
for both can be determined, only.
For a random heterogeneous soil matrix, the existence of
high permeable channels has an influence
on the effective radius and the air pressure at the well.
Thus, stochastic distributions and the average values
for both can be determined, only.
 Model situation
Model situation
 Effective radius.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
Effective radius.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
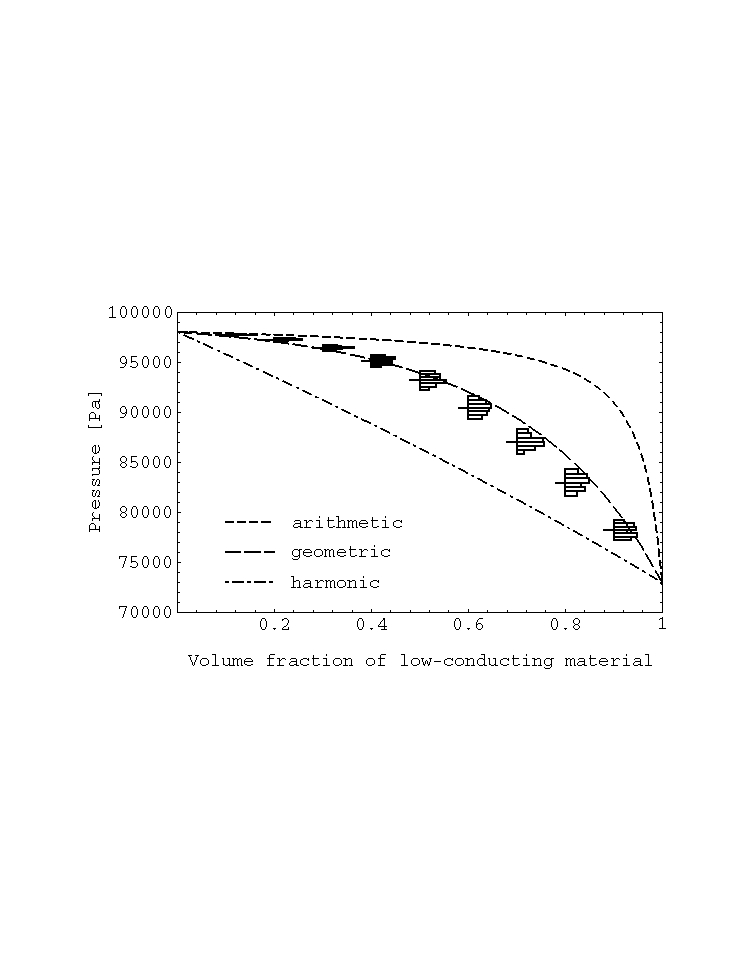 Pressure.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
Pressure.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
Conclusions
Our study has shown the following aspects:
- A highly heterogeneous soil matrix has a
larger mean value for the effective radius than a more homogeneous one.
- A large value of the depth of the domain:
- increases the standard deviation for the effective radius,
- increases the mean value for the pressure.
- Large values of the well depth increase the underpressure
at the probe.
- Large sizes of obstacles in the soil matrix
increase standard deviation for the pressure.
![]() For a random heterogeneous soil matrix, the existence of
high permeable channels has an influence
on the effective radius and the air pressure at the well.
Thus, stochastic distributions and the average values
for both can be determined, only.
For a random heterogeneous soil matrix, the existence of
high permeable channels has an influence
on the effective radius and the air pressure at the well.
Thus, stochastic distributions and the average values
for both can be determined, only.
![]() Effective radius.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
Effective radius.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)![]() Pressure.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)
Pressure.
(Well depth 2 m, depth of the domain 5 m, size of obstacles 0.125 m)